Mathematical modelling: Word problems
Year level: 3
Strand: Number
Lesson length: 60 mins
This lesson introduces students to using mathematical modelling to solve practical problems involving both additive and multiplicative relationships. Students create number sentences, select appropriate calculation strategies, and represent word problems using bar models to visually understand and solve them.
Curriculum information
Achievement standard
Students use mathematical modelling to solve practical problems involving single-digit multiplication and division, recalling multiplication facts for twos, threes, fours, fives and tens, and using a range of strategies.
Content descriptions
Students use mathematical modelling to solve practical problems involving additive and multiplicative situations including financial contexts; formulate problems using number sentences and choose calculation strategies, using digital tools where appropriate; interpret and communicate solutions in terms of the situation. AC9M3N06
Students multiply and divide one- and two-digit numbers, representing problems using number sentences, diagrams and arrays, and using a variety of calculation strategies. AC9M3N04
Students recall and demonstrate proficiency with multiplication facts for 3, 4, 5 and10; extend and apply facts to develop the related division facts. AC9M3A03
General capabilities
Numeracy
Assessment
Assess students' proficiency in using bar models to represent and solve mathematical problems by presenting an exit-ticket task. This exit-ticket task will help you gauge students' comprehension of the concepts related to bar models and their ability to differentiate between operations.
Display the exit-ticket task:
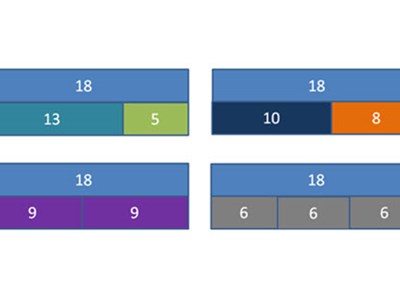
True or False? Two of these bar models can represent division and sharing. The other two cannot. But they all can represent addition and subtraction.
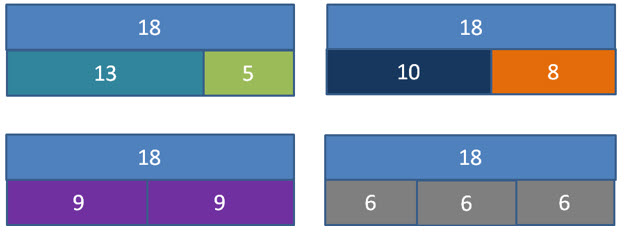
In this task, students:
- analyse each bar model and think critically about how they represent different mathematical operations
- apply their understanding of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division to determine which models can represent division and sharing
- reflect on why certain models can or cannot represent division and sharing.
To promote deeper understanding, encourage them to give their reasoning.
The statement is True: Two of these bar models can represent division and sharing, while the other two cannot. However, all models can represent addition and subtraction. Note: the answers can be found in the notes section of the presentation.
Areas of challenge
Some students may:
- need help identifying the correct relationships between quantities when creating bar models
- find it difficult to break down multi-step problems into a series of connected bars
- be challenged to translate abstract word problems into clear, accurate visual representations.
Prerequisite student knowledge and language
It is expected that students have:
- understanding of basic addition and subtraction (simple calculations that involves combining or comparing quantities)
- understanding of basic multiplication and division (simple calculations that involve grouping or partitioning quantities)
- familiarity with number sentences (write number sentences based on word problems)
- the ability to identify and represent relationships (recognise part-whole relationships and understand how to visually represent these relationships).
It is also assumed students are familiar with terms such as:
- bar model
- equal parts
- part—part whole
- difference
- altogether
- total/sum
- shared.
What you need:
Lesson plan (Word)
Teacher’s slides (PowerPoint)
Exit ticket (PowerPoint)
Learning goals
Learning intention
- We are learning to use additive and multiplicative thinking to solve maths-based problems.
- We are learning to use bar models to visually represent the quantities and relationships in a word problem.
Success criteria
By the end of this lesson, students can:
- represent everyday maths problems mathematically as number sentences
- choose and apply appropriate calculation strategies to find solutions to the problems
- use visual representations such as a bar model to illustrate their thinking and support their calculations.
Why are we learning about this?
We are learning to apply additive and multiplicative thinking to solve mathematical problems, like those we encounter every day.
The bar model is a visual tool that uses bars or rectangles to represent both known and unknown quantities. It helps students convert word problems into a clear, visual format, and acts as a bridge between the problem's context and the abstract mathematics required for a solution. By using bar models to illustrate the quantities and relationships in word problems, students can enhance their problem-solving skills.
Learning hook 10 mins
- Use the Teacher’s slides to introduce this part of the lesson.
- Refer to slide 2 to introduce the task. Ask students: What do you notice? What do you wonder? about the bar models displayed on the slide.
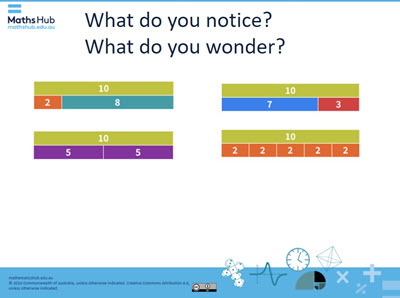
Slide 2
- Use a classroom talk to generate discussion about bar models.
- List what students notice or wonder.
Relevant number sentences
- Guide discussion to describe how bar models can be used to represent number problems. Highlight examples from the slide, prompting students to identify how the bar models correspond to different mathematical expressions.
- Discuss relevant number sentences for each bar model. Refer to slide 3, where some examples are provided.
Commutative Law of Addition
- Discuss the Commutative Law of Addition, using the example 2 + 8 = 10 and 8 + 2 = 10. Make explicit that the order of addends does not affect the sum.
Inverse relationship
- Discuss the concept of inverse relationship, using the example 2 + 8 = 10 and 10 - 8 = 2. Encourage students to think about how addition and subtraction are connected.
Multiplicative thinking
- Introduce multiplicative thinking, using the 10 5|5 model, which could represent 2 times 5 = 10 as well as 5 + 5 = 10. Discuss how bar models can help us to visualise both multiplication and addition. Discuss the inverse operation of division in relation to the bar model. Explain that if we know the total (10) and one part (5), we can find the other part by dividing the total by the known part. For instance, if we have 10 and want to find out how many groups of 5 fit into it, we can use division (10 ÷ 5 = 2).
Explore 40 mins
Introduction (10 mins)
- Use the worked example on slide 4 to illustrate a bar model with a relevant example. Talk through the problem and what each part of the bar model relates to in connection with the problem. Explain how the structure of the bar model visually represents the relationships in the problem. Present the multiple-choice question to see if students can connect the bar model to a number sentence.

Slide 4
- Use slide 5 for a further example which involves repeated subtraction or can be shown as a division. Use the multiple-choice question to gauge the class's understanding. You can also illustrate this problem on a number line, showing the initial amount and subtracting $2 for each week until it reaches zero.
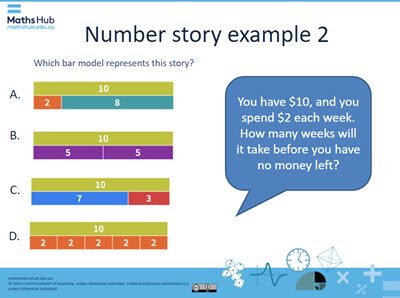
Slide 5
Activity 1: Write a number story (15 mins)
Engage students in creating word problems using bar models to reinforce their understanding of additive and multiplicative thinking.
- Ask students to choose a bar model from slide 6 and use it to write a number story (word problem).
- Encourage them to think about real-life scenarios that could be represented by the model.
- Roam the room and share students’ number stories and use as teaching moments. Pose questions such as: What real-life situation does your bar model represent? How do the numbers in your story relate to the quantities in your bar model?
Differentiation (support):
- What number story can you write for 2 + 8 =10?
- Imagine your story is about marbles. If you started with 2 marbles and you added 8 marbles, how many marbles altogether?
- Can you think of a different story?
Differentiation (extension):
- Can you think of a subtraction story for each bar model?
- Which one is the most challenging story to create? Why?
Activity 2: Represent a word problem as a bar model (15 mins)
Reinforce students’ understanding of bar models by representing word problems visually, identifying the mathematical relationships.
- Ask students to choose a word problem from slide 7.
- Make explicit that students draw a bar model that visually represents the quantities and relationships described in their chosen word problem. Encourage them to label the total and the individual parts clearly.
- As students work on their bar models, roam the room to provide support and feedback.
- Use slides 8, 9 and 10 to discuss each word problem and the relevant bar model.
Differentiation (support)
- For students building their confidence, direct them to Problem 1 or Problem 2, which involve one-step problems that focus on additive thinking. Provide guided support to help them create their bar models.
Differentiation (extension)
- For students ready for a challenge, refer them to Problem 3, which is a two-step problem involving both addition and subtraction. Encourage them to think critically about how to represent the two steps in their bar model.
Summary and reflection 5 mins
Summarise the lesson’s key points and invite students to reflect on what they’ve learned:
- Ask them about what they now know about bar models.
- In their maths journals, have students write down one thing they now know about using bar models.
- Discuss as a class how this knowledge might help them solve problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division in the future.