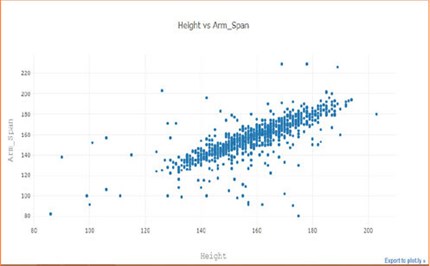
reSolve: Algorithmic thinking – Data visualisation
This unit teaches students to use modern tools and methods to describe and find relationships in large, authentic, real-world datasets, including the World Bank Open Data for global development. The unit shows how computer-based information visualisation and data analysis can help us to find and to better understand complex relationships in our world. Activities follow a 'journey of discovery' that interprets raw data by applying different visualisation methods.
Additional details |
|
| Year level(s) | Year 9, Year 10 |
|---|---|
| Audience | Teacher |
| Purpose | Teaching resource |
| Format | Downloadable resources |
| Teaching strategies and pedagogical approaches | Mathematics investigation |
| Keywords | data representation, algorthmic thinking |
Curriculum alignment |
|
| Curriculum connections | Technologies, Numeracy, STEM/STEAM |
| Strand and focus | Statistics, Build understanding, Apply understanding |
| Topics | Data representation and interpretation |
| AC: Mathematics (V9.0) content descriptions |
AC9M10ST02
Compare data distributions for continuous numerical variables using appropriate data displays including boxplots; discuss the shapes of these distributions in terms of centre, spread, shape and outliers in the context of the data
AC9M10ST03
Construct scatterplots and comment on the association between the 2 numerical variables in terms of strength, direction and linearity
AC9M10ST04
Construct two-way tables and discuss possible relationship between categorical variables
AC9M9ST03
Represent the distribution of multiple data sets for numerical variables using comparative representations; compare data distributions with consideration of centre, spread and shape, and the effect of outliers on these measures
AC9M9ST05
Plan and conduct statistical investigations involving the collection and analysis of different kinds of data; report findings and discuss the strength of evidence to support any conclusions?
AC9M10ST01
Analyse claims, inferences and conclusions of statistical reports in the media, including ethical considerations and identification of potential sources of bias |
| Numeracy progression |
Interpreting and representing data (P8)
|
Copyright details |
|
| Organisation | ReSolve: Maths by Inquiry |
| Copyright | © Australian Government Department of Education, Skills and Employment 2021. Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0. |
Related resources
-
reSolve: Statistics: Student Profiling
A series of inquiry-based lessons where students explore the Census@School data and create a student profile.
Resource details -
Interpret and discuss data displays: Year 10 – planning tool
This planning resource for Year 10 is for the topic of Interpret and discuss data displays.
Resource details -
Statistical analysis: Year 10 – planning tool
This planning resource for Year 10 is for the topic of Statistical analysis.
Resource details -
Off the scale
This lesson introduces students to the idea of a log scale, a seemingly perplexing way to present data. The lesson begins with an exploration of examples when a linear scale is inappropriate and concludes with a plotting activity using authentic data from the COVID-19 pandemic.
Resource details